Demystifying Data Professionals: A Spider Web Diagram Analysis
In the age of information, data has become a valuable asset for businesses across various industries. As a result, the demand for skilled data professionals has soared. However, the different roles within the field can often be confusing, with titles like Data Engineer, Machine Learning Engineer, Data Scientist, and Data Analyst being used interchangeably. To shed light on these distinct specialties and help clarify their roles, I stumbled upon a captivating spider web diagram on the internet. In this blog post, we will delve into the diagram's significance and how it helps us understand the differences between various data professionals.
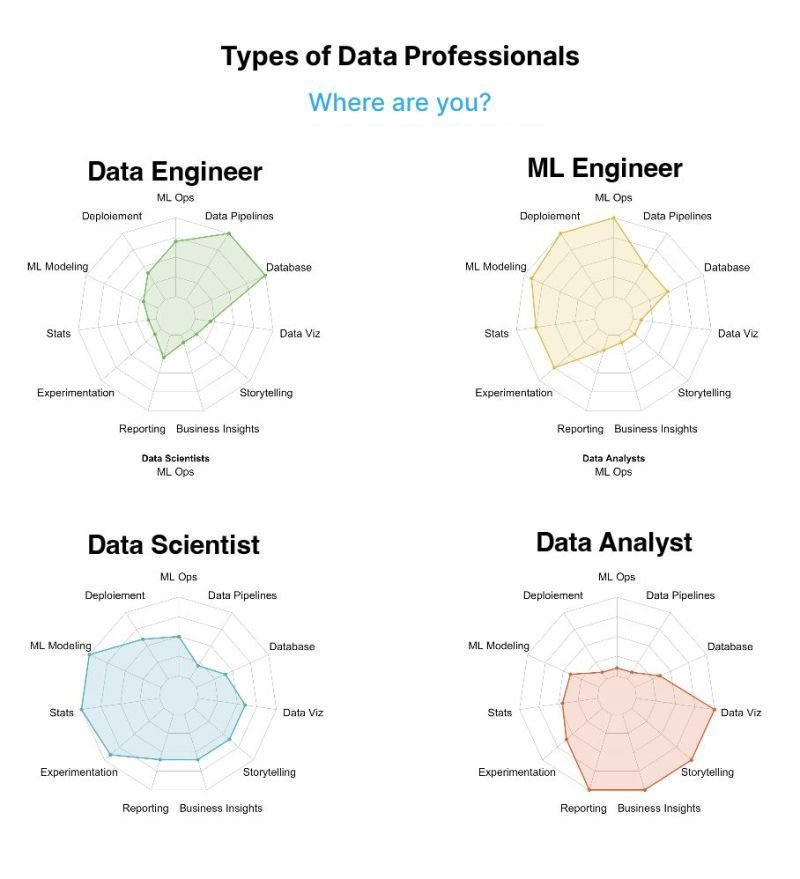
Understanding the Spider Web Diagram: The spider web diagram presents a visual representation of different data areas, with each specialty weighed in terms of their expertise in those areas. Let's explore the key data areas highlighted in the diagram and how each type of data professional contributes to them:
ML Ops: Machine Learning Operations (ML Ops) refers to the practices and tools used to manage and deploy machine learning models. While all data professionals may have some involvement in ML Ops, Machine Learning Engineers specialize in this area. They possess the technical skills necessary to build scalable and efficient ML systems.
Data Pipeline: Data Engineers play a pivotal role in constructing and maintaining data pipelines. They focus on the collection, cleaning, and transformation of data, ensuring that it flows seamlessly through various stages, ultimately leading to valuable insights. They work closely with Data Scientists and Machine Learning Engineers to ensure a smooth data flow for model development and analysis.
Database: Data storage and management are critical components of any data-driven organization. Data Engineers are responsible for designing and maintaining robust databases that facilitate efficient data retrieval, storage, and querying. They ensure data integrity, security, and accessibility while optimizing performance.
Data Visualization and Storytelling: Data Visualization and Storytelling play vital roles in conveying insights effectively. Data Analysts and Data Scientists possess expertise in visualizing data in a meaningful and impactful manner. They utilize tools and techniques to present complex information through interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards, enabling stakeholders to grasp key insights easily.
Business Insight and Reporting: Data Analysts and Data Scientists often collaborate to extract valuable business insights from raw data. They apply statistical techniques and exploratory data analysis to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations. By generating comprehensive reports and presenting actionable recommendations, they aid decision-making processes within organizations.
Experimentation: Data Scientists, in collaboration with other data professionals, design and conduct experiments to validate hypotheses and test models. They develop methodologies, perform A/B testing, and evaluate outcomes to iteratively refine models and improve predictive accuracy.
Statistics: Statistical analysis forms the foundation of data-driven decision-making. Data Analysts and Data Scientists possess a solid understanding of statistical concepts and methods. They employ statistical techniques to draw meaningful inferences, validate assumptions, and quantify uncertainties in data.
Machine Learning Modeling: Machine Learning Engineers and Data Scientists excel in the domain of machine learning modeling. They leverage algorithms, statistical techniques, and vast amounts of data to build predictive models, optimize performance, and enable intelligent automation.
Development: Data Engineers and Machine Learning Engineers often possess strong programming skills. They specialize in developing scalable and efficient code that supports data processing, analysis, and model deployment. Their coding expertise ensures the smooth functioning of data systems and applications.
The spider web diagram provides a valuable framework for understanding the differences between various data professionals. By highlighting their respective expertise in different data areas, the diagram helps clarify the unique contributions of Data Engineers, Machine Learning Engineers, Data Scientists, and Data Analysts. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for organizations seeking to build effective data teams and harness the full potential of their data assets.